In this article, we'll see what Spread and Rest Operator is ..?, but before diving into it we will first see What Destructuring in javascript is..?
Let's dive in!
Destructuring
What Destructureing means..?
The Destructuring syntax is a JavaScript expression that makes it possible to unpack values from arrays, or properties from objects, into distinct variables.
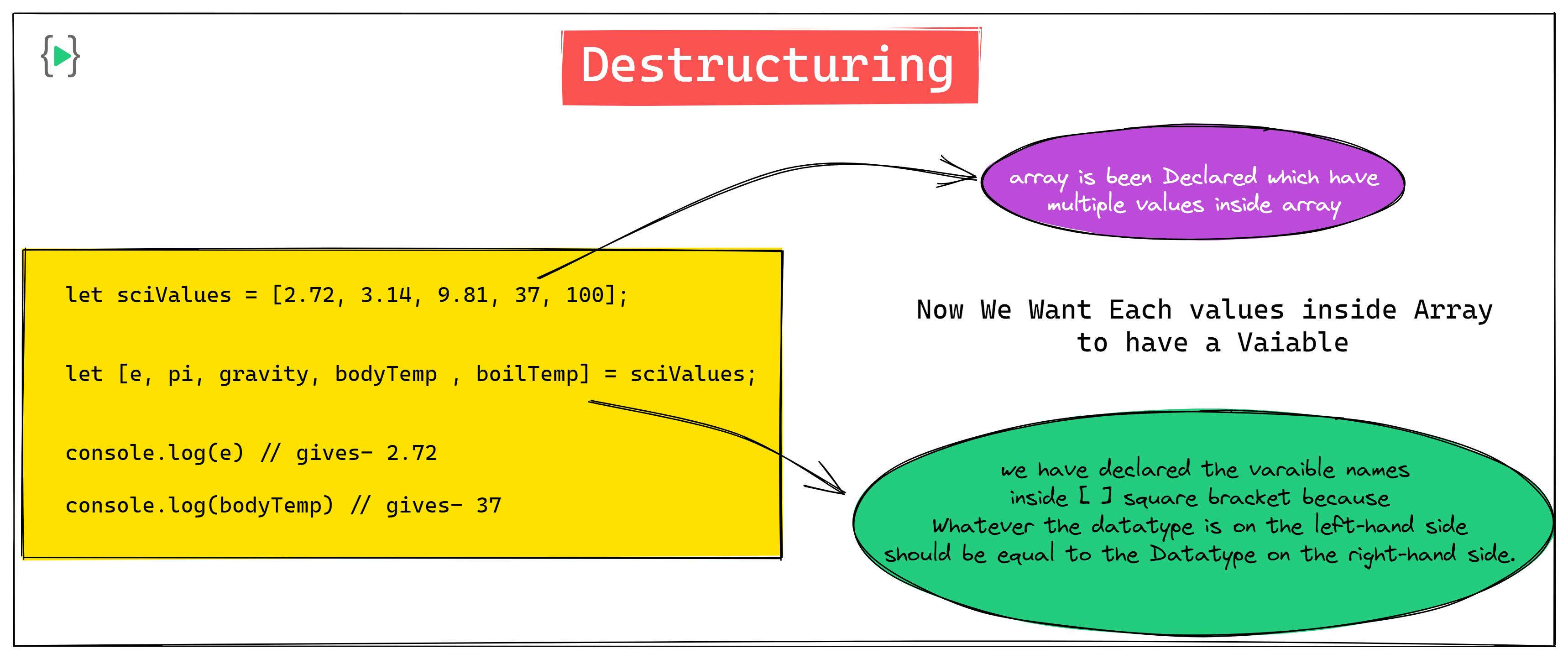
In Simple Words, Destructuring means, when we have values inside Array and we want that value to get stored inside a variable
let sciValues = [2.72, 3.14, 9.81, 37, 100];
now we want each value inside the Array to give to a different variable. we can give variables in a below-mentioned way also
let e = sciValues[0] // gives - 2.72
let Pi = sciValues[1] // gives - 3.14
but, this is not the scenario, when we have too many array values and we want to give each array value a variable, so the above methods will be not the best to use . so this is where Destructuring Comes into the Picture.
let sciValues = [2.72, 3.14, 9.81, 37, 100];
let [e, pi, gravity, bodyTemp , boilTemp] = sciValues;
console.log(e) // gives- 2.72
console.log(bodyTemp) // gives- 37
Whatever the datatype is on the left-hand side should be equal to the Datatype on the right-hand side.
Above You have seen Destructuring of Array, now we will see How we can Destructure using
Object..?
Destructureing Using Objects
let me explain with an example first
let userDetails = {
name: "Hitesh",
courseCount: 5,
role: "admin"
}
consoe.log(userDetails.name) // Hitesh
This is how we get values many a time from Objects, but if we want to use 50 Times after this would be the long code to print, so we will Destructure this Object
let userDetails = {
name: "Hitesh",
courseCount: 5,
role: "admin"
}
let {name, couseCount, role} = userDetails
console.log(name) // Hitesh
console.log(role) // admin
Important note: In
object Destructuringthe variable should have theobject value keyname as Variable. likename ,courseCount ,admin
So, this is what Destructuring in Javascript is. Now Let's See Rest and Spread Operators
before starting Rest and Spread Operator let me give You a Hint✨.
...args, ...Hitesh, ...numbers, ...anythings
Anything After
...these three dots arespread and Rest Operator.So what's the difference between them..?So the Difference is what the challenge we are facing.? on the bases of that it automatically changes whether to use the
spread Operator or Rest Operator
Spread Operator
Spread syntax (...) allows an iterable, such as an array or string, to be expanded in places where zero or more arguments (for function calls) or elements (for array literals) are expected.
Spread syntax can be used when all elements from an object or array need to be included in a new array or object, or should be applied one-by-one in a function call's arguments list.
let's seen an example to get what exactly the spread operator works.
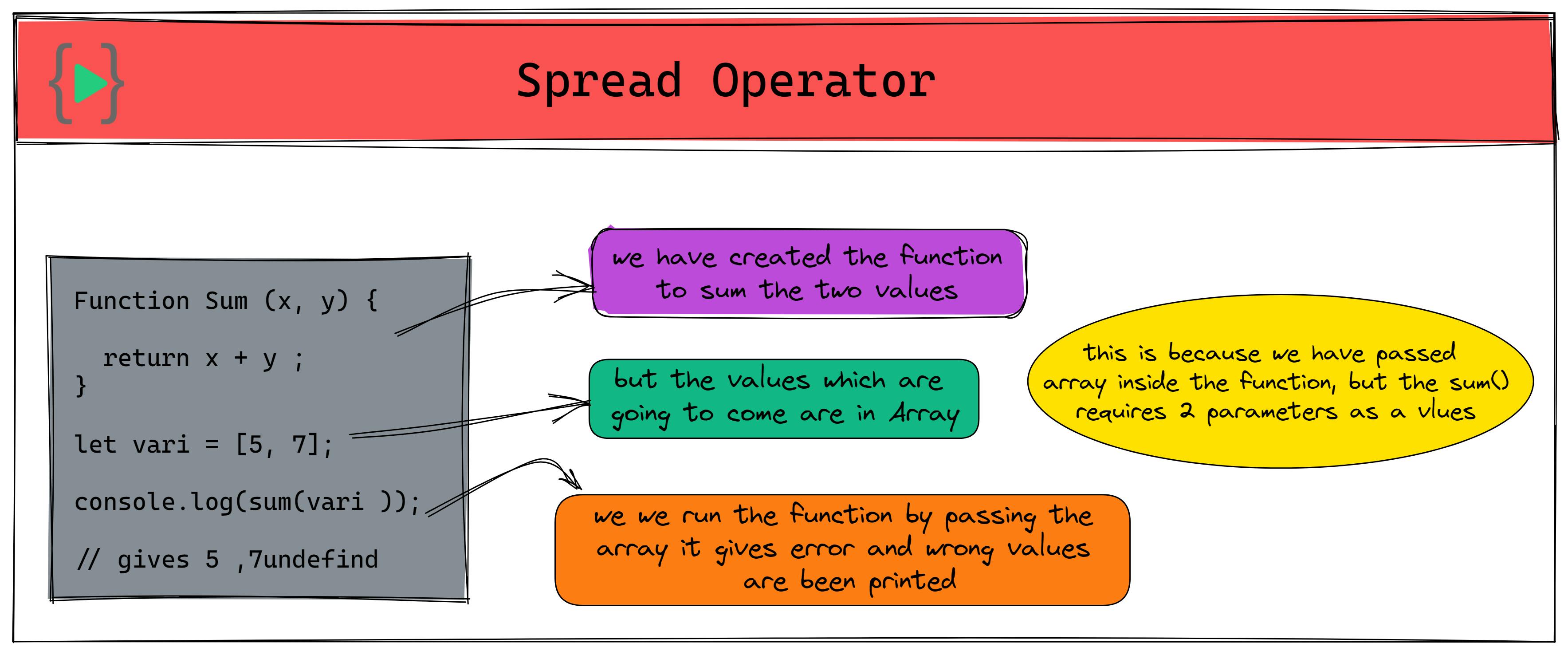
We have created a function to sum two Values, and the values are stored in an array, how would we put these values in the function let's see
Function Sum (x, y) {
return x + y ;
}
let vari = [5, 7];
console.log(sum(vari )); // gives 5 ,7undefind
to pass the values of the array one by one inside the function we here will use Spread Operator.
Function Sum (x, y) {
return x + y ;
}
let vari = [5, 7];
console.log(sum(...vari )); // gives 12
here we have passed the array ..vari inside a function using ...vari which iterates the values of the array one by one and passes it into the function Sum()
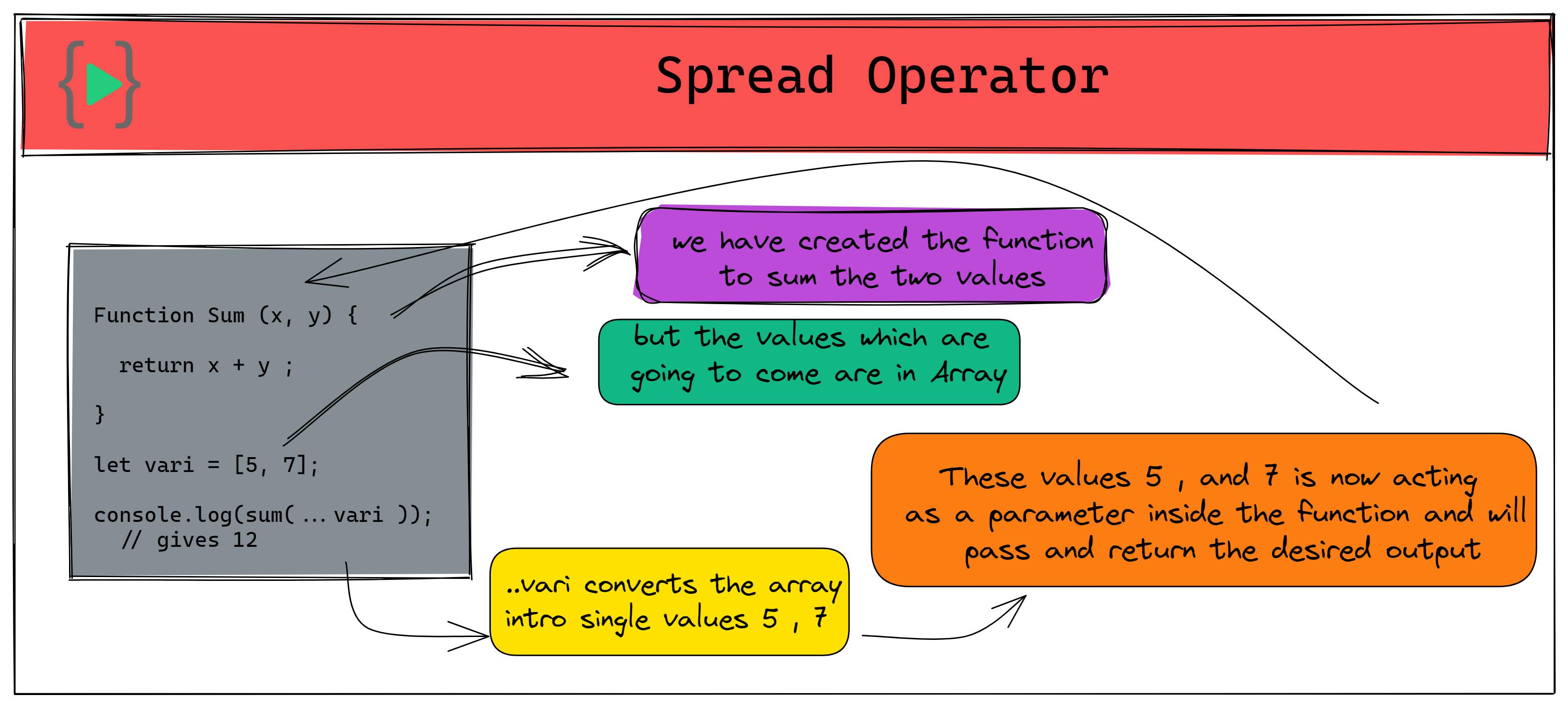
This is how Spread Operator Works, it destructures the array elements into different values.
for more detail Overview check MDN Spread Operator Docs
Rest Operator
The rest parameter syntax allows a function to accept an indefinite number of arguments as an array, providing a way to represent variadic functions in JavaScript.
Rest Operator is initialize with ...values
Let's first see the example of how the rest operator works..?
function myFun(a, b, ...manyMoreArgs) {
console.log("a", a);
console.log("b", b);
console.log("manyMoreArgs", manyMoreArgs);
}
myFun("one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six");
// a, "one"
// b, "two"
// manyMoreArgs, ["three", "four", "five", "six"] <-- notice it's an array
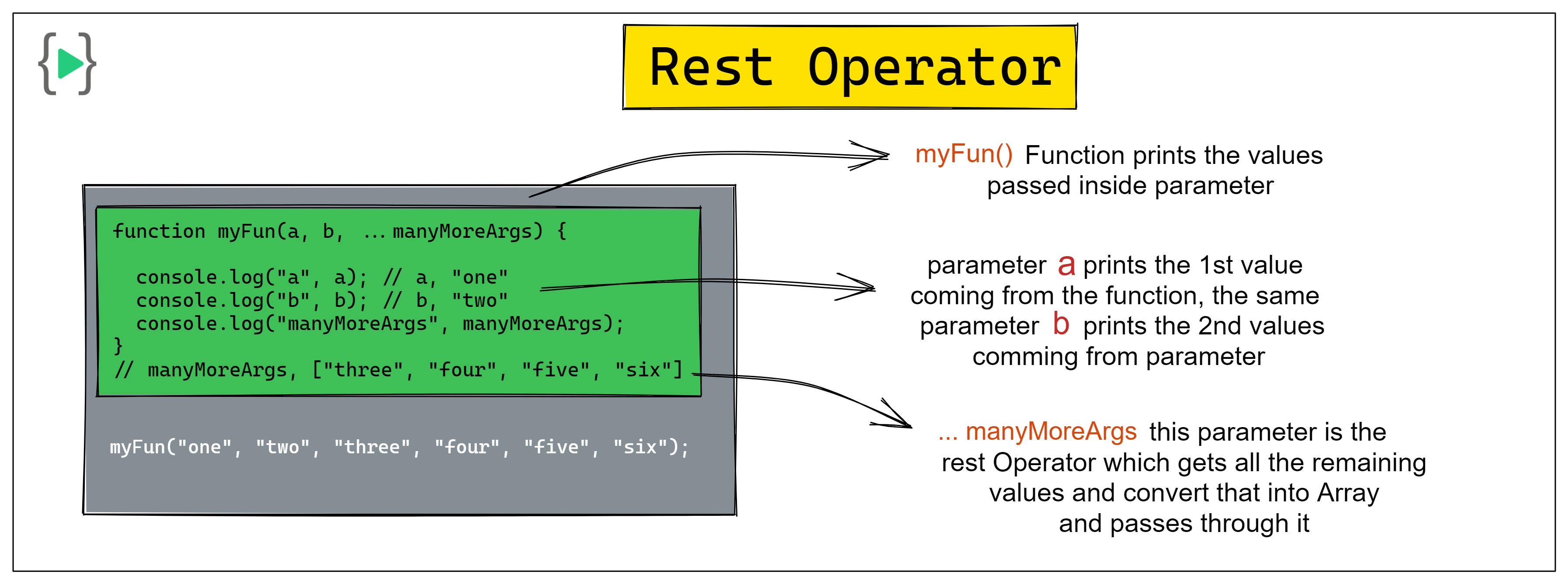
In this above example, the first argument is mapped to "a" and the second to "b", so these named arguments are used as normal.
However, the third argument, manyMoreArgs , will be an array that contains the third, fourth, fifth, sixth, …, nth— as many arguments that the user includes.
This ...manyMoreArgs converts the values into an Array. That's why ES6 introduced the Rest Parameter to make a code much more readable.
limitations
Rest parameters take all the remaining arguments of a function and package them in an array. That naturally brings two limitations.
- You can use them max once in a function
- multiple rest parameters are not allowed.
Conculsion
Rest and Spread Operators both have to use the same syntax . . ..But both of them are totally different, Spread (the name suggests it open out) Operator spreads the Array into Elements. Where Rest (as the name suggests remaining) Operator collects all the elements and stores them into an Array.